Research Activities
NSF MRI Grant: 2216332
NSF MRI Grant: 2216332, "Development of a Terahertz Measurement Facility for Wireless Communications, Electronics and Materials," awarded in October 2022 and led by PI Prof. Theodore S. Rappaport (NYU), has enabled the establishment of a state-of-the-art measurement facility, the "THz Lab," supporting measurements up to 330 GHz.

New York University
The multi-user THz measurement facility
A new THz measurement facility (THz Lab) has been established at the NYU WIRELESS Research Center in Room 915. The THz Lab provides measurement capabilities from DC to 330 GHz for RF circuits, devices, and antennas fabricated on semiconductor wafers and dies.
In May of 2024, two prominent manufacturers of semiconductor wafer probing solutions: FormFactor and MPI Corporation, each delivered their version of the world's first four-port manual probe station. MPI Corporation and FormFactor worked closely with the THz Lab team to finalize the designs and have successfully realized the concepts into reality. The probing system allows measurement of on-chip devices and circuits simultaneously from East, West, North, and South directions around the wafer or die. Both stations are now setup and fully operational providing measurement capabilities up to 330 GHz using frequency extenders from Virginia Diodes Inc. and the Keysight N5247B PNA-X four-port network analyzer.
The complete inventory of the THz Lab can be viewed on the Equipment page.
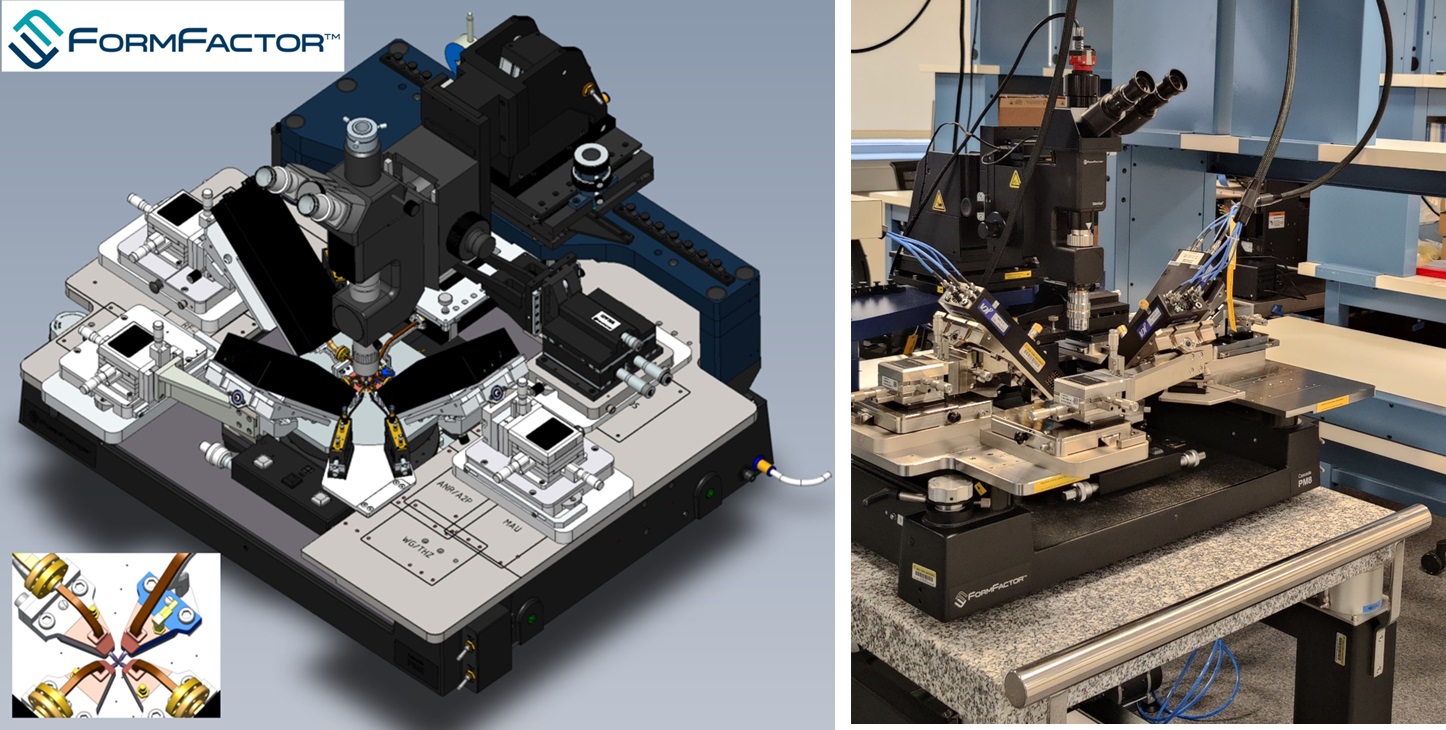
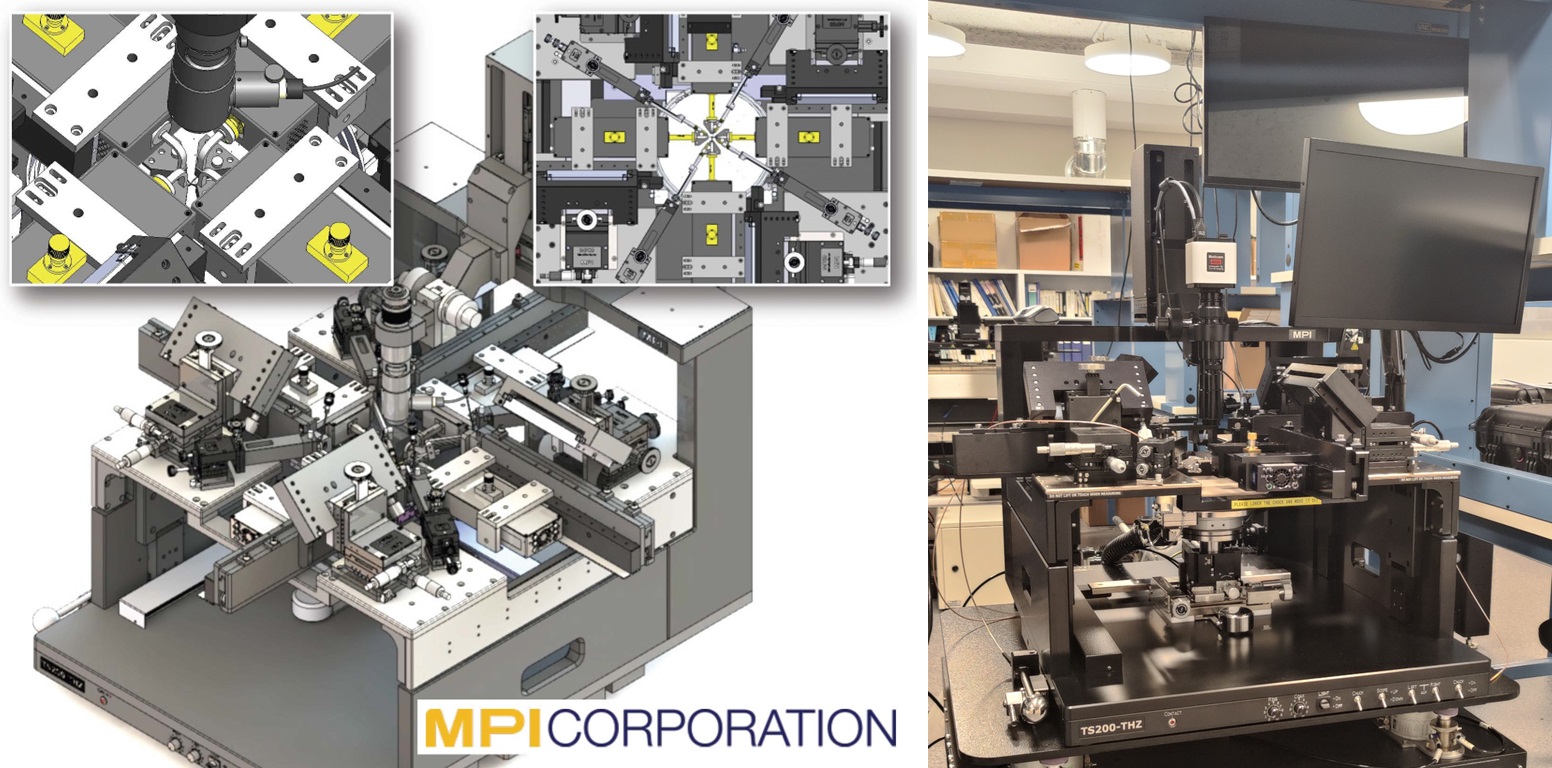
On-chip SOLR calibration standards for simultaneous four-port probing
True four-port probing at mmWave and beyond is anticipated to enable future multi-band wireless devices using several antennas and RF chains. However, there is limited knowledge about on-chip orthogonal port calibration techniques at mmWave and THz frequencies. Ph.D. student, Dipankar Shakya, with support from undergraduate students Ethan Shieh and Brenden Ngai, completed the design and tape-out for on-chip Short-Open-Load-Reciprocal (SOLR) calibration beyond 100 GHz in UMC's 28 nm CMOS process.
NYU VIP-300X Wireless 6G course
 Alongside the development of the THz Lab, in the fall 2023 semester, a new undergraduate course was introduced to leverage the simulation and measurement resources of the THz measurement facility at NYU WIRELESS under the guidance of Prof. Michael E. Knox. The students enrolled in this course, VIP-300X Wireless 6G, are part of the Vertically Integrated Projects (VIP) curriculum consisting of multi-year, multidisciplinary projects that emphasize innovative and research-active education. The VIP program opens opportunities for students to develop professionally valuable skills while making real-world contributions while earning academic credit.
Alongside the development of the THz Lab, in the fall 2023 semester, a new undergraduate course was introduced to leverage the simulation and measurement resources of the THz measurement facility at NYU WIRELESS under the guidance of Prof. Michael E. Knox. The students enrolled in this course, VIP-300X Wireless 6G, are part of the Vertically Integrated Projects (VIP) curriculum consisting of multi-year, multidisciplinary projects that emphasize innovative and research-active education. The VIP program opens opportunities for students to develop professionally valuable skills while making real-world contributions while earning academic credit.
The 11 undergraduate students enrolled, started by designing and building high frequency four-port devices and testing those devices on a VNA. In order to prepare for the installation and operation of the probe stations, the students investigated various calibration techniques required to properly characterize devices with non-coaxial terminations. The instructional strategy, which began with lower-frequency designs and gradually advanced to higher frequencies, has helped students build confidence and proficiency in both fabrication and high-frequency measurement techniques.
Cryogenic Microwave Probe Development at NYU
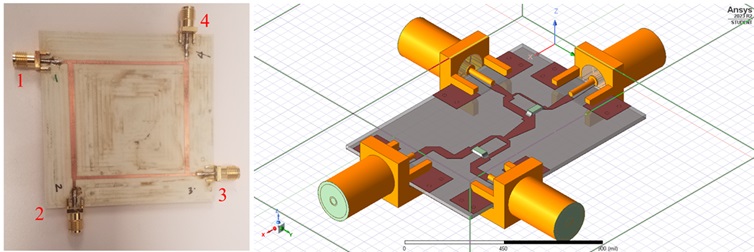
Under the NSF-MRI program, the team at NYU under Prof. Davood Shahrjerdi, is developing a novel microwave probe compatible with cryostats, enabling measurements from room temperature down to 1.5 K. This initiative addresses the critical need for faster turnaround times in testing and characterizing cryogenic microwave electronics for quantum information science and quantum network technologies. Unlike traditional dilution refrigerators with long cooling cycles, cryostats offer a significantly quicker cooldown, making them ideal for rapid prototyping.
The team has focused on designing and fabricating the first prototype of a dedicated shielding cavity to house the device under test (DUT). This cavity is engineered to securely hold the DUT, provide electrical interconnection via CPW circuits on PCBs, shield the DUT from radiation and electromagnetic loss, and integrate cryogenic temperature sensing and local heating for precise temperature control. Ph.D. student Miguel Manzo-Perez and undergraduate student Dalilah Mostoslavsky have been actively involved in this development, gaining valuable experience in high-frequency electromagnetic simulations and superconducting CPW resonators. Miguel is leading the probe fabrication and cryogenic testing, while Dalilah's involvement has shaped her academic trajectory towards quantum information science.

Publications
- D. Shakya, T. S. Rappaport, E. Shieh, M. E. Knox, H. Rahmani, D. Shahrjerdi, M. Ying, K. Fan, M. Lu, A. Rumiantsev, V. Mallette, G. Fisher, G. De Chirico, P. Ghate, and S. McMahon, "Four-Port Probe Stations and SOLR Calibration Standard Design up to 125 GHz on 28 nm CMOS," (Submitted) Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (AMPC) 2025, Jeju, S. Korea, 2025, pp 1-3.
- M. Manzo-Perez, M. Jamalzadeh, M. Nguyen, C. Nadeau, A. Madden, I. Shiravand, K. Kisslinger, X. Tong, K. Sardashti, M. Senatore, M. LaHaye, D. Shahrjerdi, "Physical patterning of high-Q superconducting niobium resonators via ion beam etching," (Submitted) Applied Physics Letters, 2025.
Florida International University
High-Performance SDR System for 135-150 GHz Communication
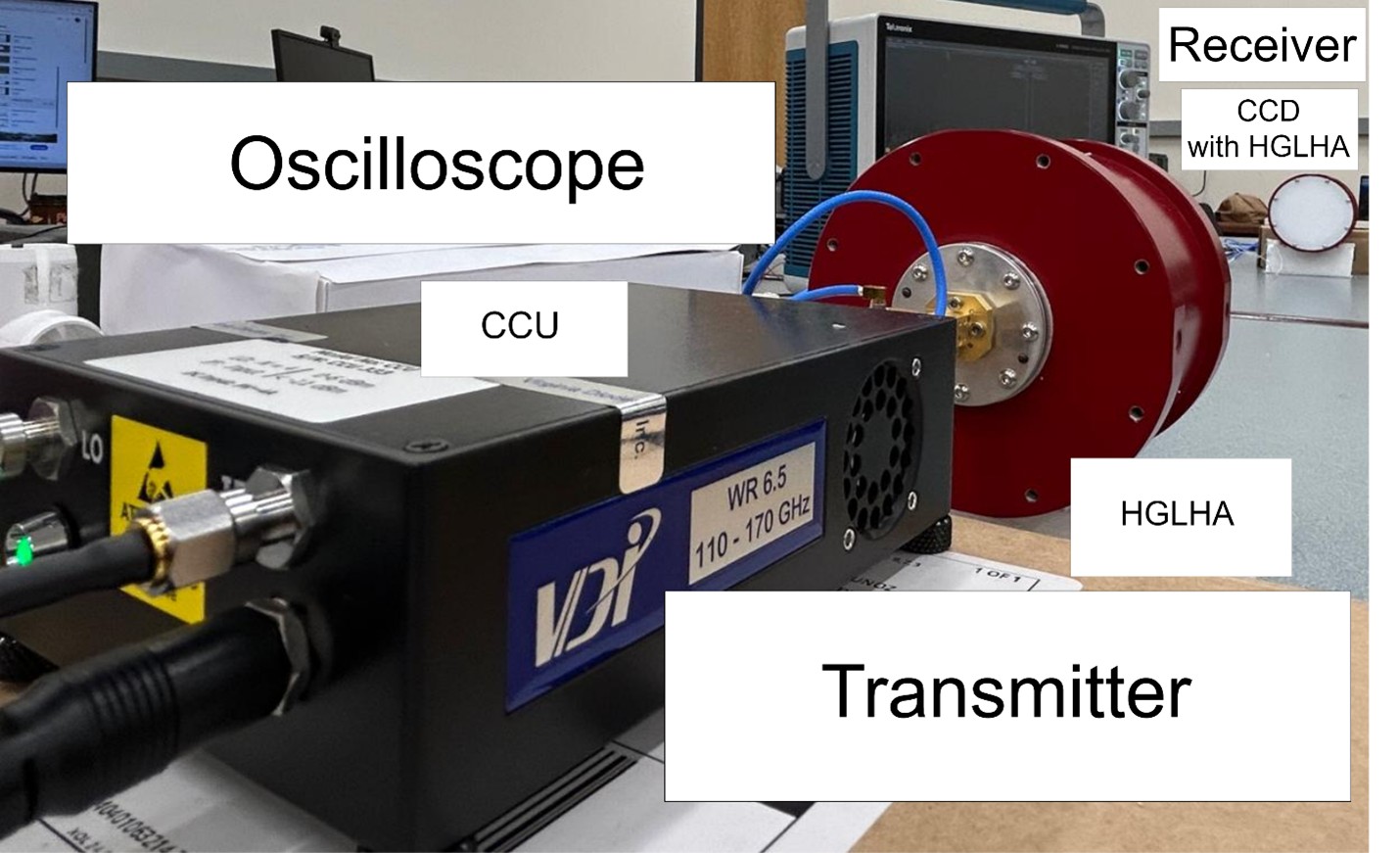
The research at FIU focuses on the design and development of a cutting-edge Software-Defined Radio (SDR) system operating in the 135-150 GHz frequency range. Leveraging I/Q modulation techniques such as Differential Binary Phase Shift Keying (DBPSK), the system integrates advanced components, including Virginia Diodes (VDI) compact upconverter and downconverter, high-gain 40 dBi lens horn antennas, and the Xilinx RFSoC ZCU111 for real-time digital signal processing.
The system achieves a 64 Mbps data rate over a 500 MHz intermediate frequency (IF) with a 64 MHz baseband bandwidth. At 20 dBm transmit power on a 147 GHz channel, we measured an impressive 55 dB signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at 1 m, with simulations predicting viable 64 Mbps communication at distances up to 2 km for a BER of <10⁻³.
Designed on the Xilinx PYNQ platform, the SDR features a user-friendly interface and is optimized for applications like vehicle-to-vehicle communication, backhaul networks, and data center interconnects. Key challenges addressed include synchronization, signal integrity, and environmental sensitivity, ensuring robust performance even in complex wireless environments.
Joint Communications and Sensing (JCAS): D-band and 5.8 GHz ISM
FIU explored JCAS using 5.8 GHz Industrial, Medical, Scientific (ISM)
spectrum with D-band spectrum, for data communications using a software-defined radio (SDR) approach, where range and direction information is recovered through real-time cross correlation methods across multiple simultaneous receive beams in a single shot. Here, a multifrequency active repeater technique was proposed, where the uplink is at the D-band, and the downlink occurs at 5.8 GHz ISM band. The proposed multi-frequency ISM+D-band solution allows secure and safe command and control of a UAS while allowing location and enhanced security using JCAS in a GPS denied environment.
Publications
- Madanayake, A and Lawrance, K and Kumarasiri, U and Sen, P and Cintra, R J and Karunanayake, K and Sivasankar, S. (2025). Joint Communication and Sensing at D-Band SDR and at 5.8 GHz via Multibeam Arrays. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques. 73 (6) 3236 to 3249
University of Nebraska-Lincoln
Diffuse scattering modeling of near-field propagation channel at THz band with reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS)
The research at UNL studies the method of angular spectrum representation to express an arbitrary field as a superposition of plane (and evanescent) waves, each having varying amplitudes and propagation directions.
Design and characterization of dual-band complementary split-ring resonator arrays in the D-band (110–170 GHz)
Ph.D. student, Laxmi Chapagain, has designed and compared different machine learning models to optimize bandwidth for joint communication and sensing for multi-band complementary split-ring resonator arrays in the D-band.
Spectrum allocations for 6G and beyond
In collaboration with PI Rappaport, UNL conducted an in-depth analysis of recent regulatory rulings and spectrum preferences issued by international standard bodies such as the International Telecommunications Union and Federal Communications Commission as they seek to identify feasible bands for future wireless networks.
Publications
- L. Chapagain and S. Nie, "Design and Characterization of Dual-Band Complementary Split-Ring Resonator Array in the D-Band for 6G Wireless Networks," MILCOM 2024 - 2024 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Washington, DC, USA, 2024, pp. 276-281, doi: 10.1109/MILCOM61039.2024.10773912.
University of Colorado Boulder
At UC Boulder, the research efforts are centered on designing active circuits at W-band and beyond, utilizing advanced semiconductor technologies such as Gallium Nitride (GaN) and Gallium Arsenide (GaAs). The team has successfully designed and characterized several circuits, with measurements primarily performed on-wafer. A significant aspect of their work involves developing robust calibration structures and methods to eliminate resonances caused by substrate modes.
Key achievements include the design and validation of various W-band (75-110 GHz) circuits fabricated in HRL T3 GaN technology. These circuits have been rigorously measured in the UC Boulder laboratory and further validated at AFOSR.
Significant progress has been made in developing front-end components for full-duplex communications, including the integration of a passive circulator with a Power Amplifier (PA) and Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) using the HRL T3 mm-wave GaN process. Furthermore, they fabricated GaAs on-wafer calibration standards in a WIN process, successfully demonstrating the presence of cross-talk resonances and identifying methods to eliminate them.
Publications
- Romano, Anthony and James, Grant and Gilbert, Ryan and Miller, Nicholas C and Johannes, Seth and Popović, Zoya. (2025). Integrated 75–100 GHz In-Band Full-Duplex Quasi-Circulator-Based Front-End GaN MMIC. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques. 73 (6) 3121 to 3132.

