A Journey of STAR-DDS: Anti-VEGF Drug Delivery System for the Eye
Speaker:
Jennifer J. Kang-Mieler, PhD
Professor and Chair
Dept. of Biomedical Engineering
Stevens Institute of Technology
Abstract:
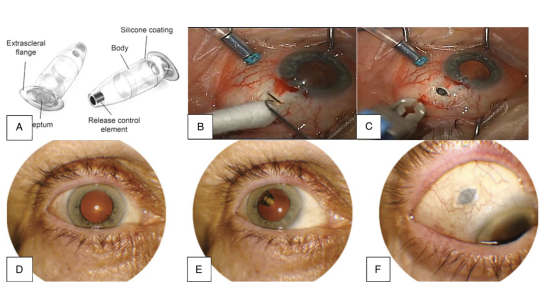
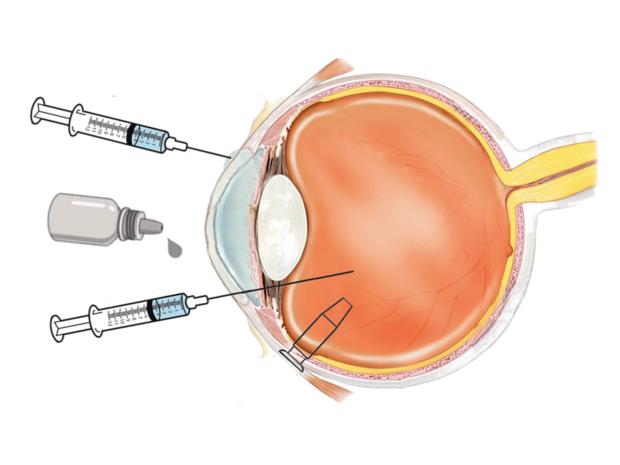
Dr. Kang-Mieler’s research projects include ocular drug delivery, retinal imaging and biomarkers, retinal hemodynamics, and electrophysiology. Her clinical interests include retinal vascular diseases. In this talk, she focuses on the role of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in ocular diseases, including age-related macular degeneration (AMD) with choroidal neovascularization (CNV) and diabetic retinopathy (DR). VEGF has been identified as a key regulator of angiogenesis, both acting as an endothelial cell mitogen and increasing vascular permeability. Landmark clinical studies demonstrated that anti-VEGF agent therapy (ranibizumab or aflibercept) was remarkably efficacious for AMD with CNV and DR; these drugs are now the gold standard treatment for these diseases. However, a major limitation for these treatments is that repeated dosing is required every four to six weeks. Frequent dosing is undesirable for a variety of reasons including: decreased patient comfort, increased likelihood of complications and bolus administration of the agent. Consequently, there is a great need to develop a more effective, long-lasting, relatively non-invasive delivery method for anti-VEGF agents. Dr. Kang-Mieler’s laboratory has created a Sustained Treatment with Anti-VEGF agents for Retinal diseases - Drug Delivery System (STAR-DDS), which utilizes biodegradable drug loaded-microspheres embedded into a biodegradable thermo-responsive hydrogel. This presentation will discuss the advantages of the STAR-DDS platform, including the safety and efficacy.
Dr. Kang-Mieler received her BA in Mathematics, MS in Applied Mathematics, and PhD in Biomedical Engineering from Northwestern University. After completing a post-doctoral fellowship at the University of Illinois at Chicago in the Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences she joined the Illinois Institute of Technology as a member of the biomedical engineering faculty. In the summer of 2022, she accepted an offer from the Stevens Institute of Technology. Dr. Kang-Mieler is a Fellow of the American Institute for Medical and Biological Engineering (AIMBE) and the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO), where she served as Vice President and Board of Trustees. At NIH she the current Chair of the Brain Imaging, Vision, Bioengineering, and Low Vision Technology Development (BIVT) panel.