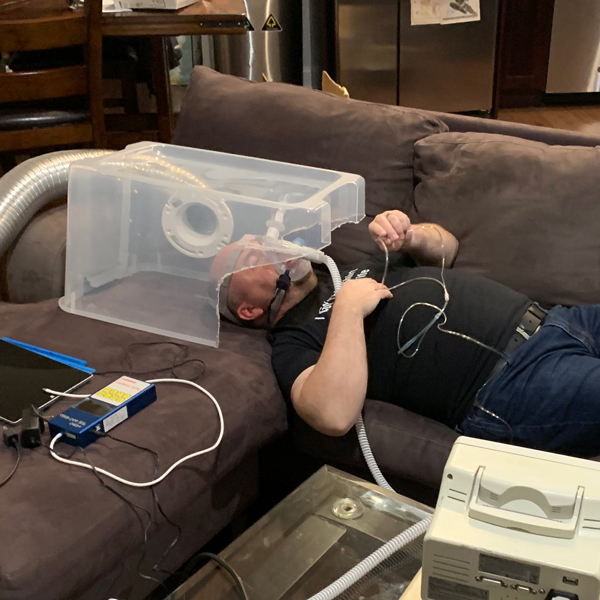
AirVENT: Test Results for Negative Pressure Hood
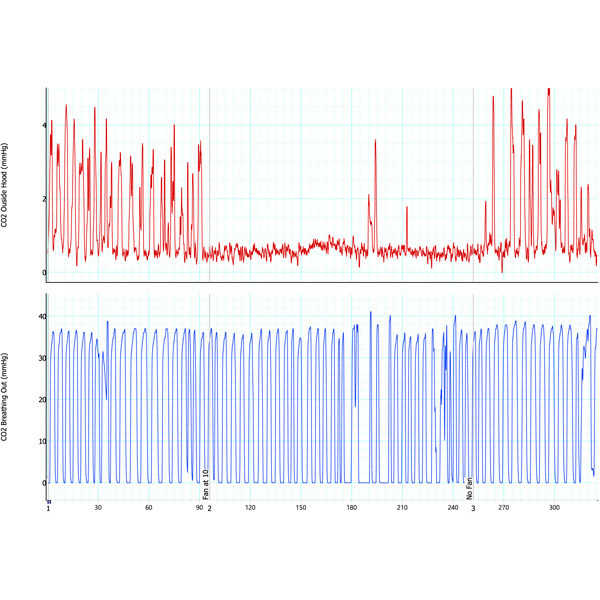
Attached is a screen shot of one test showing the effectiveness of the hood to scavenge expired CO2. The top panel in the graph shows CO2 levels being measured from just outside the hood. The lower panel in the graph shows the CO2 being sampled at the experimenter’s (Dr. Serrador) nose, i.e., in the exhale. The first 90 seconds (horizontal axis units in seconds) shows measurements with the fan of the negative pressure hood off. In the lower panel of the graph, the expired CO2 peaked at about 36-38 mmHg (~5%), which is considered normal. The peaks outside the hood were ~3-4 mmHg (top graph) or ~10% of the expired breath. This is a substantial amount of molecules (~1.3x1017). At ~95 seconds the fan of the hood was turned on. As seen in the lower panel of the graph, the turning on of the hood fan did not affect the amount of CO2 being exhaled out. However, the peaks completely disappeared in the upper graph indicating that the CO2 was no longer present outside the hood and that this negative pressure hood was effectively scavenging the expired CO2. At ~250 sec the fan was turned off and then the CO2 can be seen peaking outside the hood (top graph) return.
The two peaks in the middle of the graph on tops panel occurred when experimenter leaned out of the hood a little bit to answer some questions from his brand new research assistant (Dr. Serrador’s wife Jen assumed the role of his research assistant as the project is being conducted during the Covid-19 shelter in place order!).

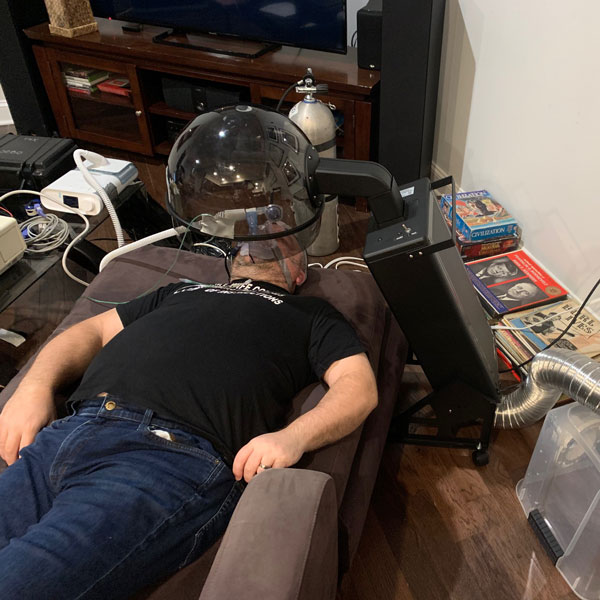
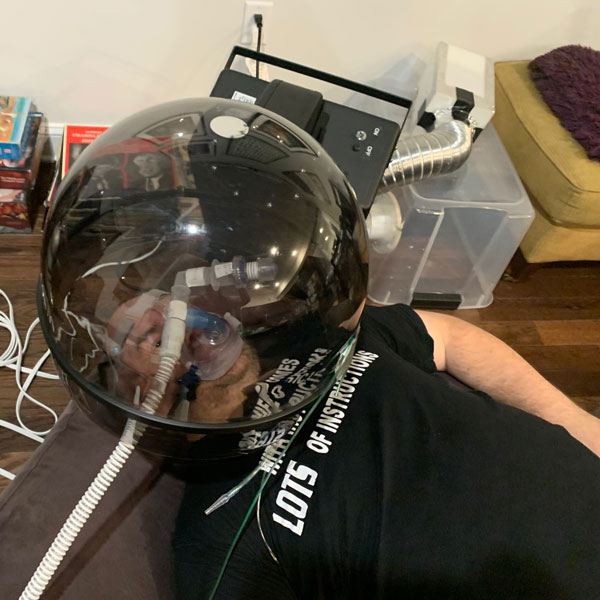
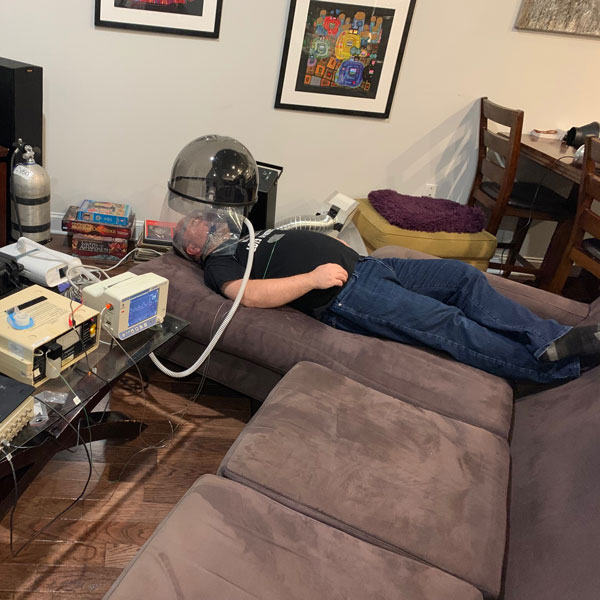
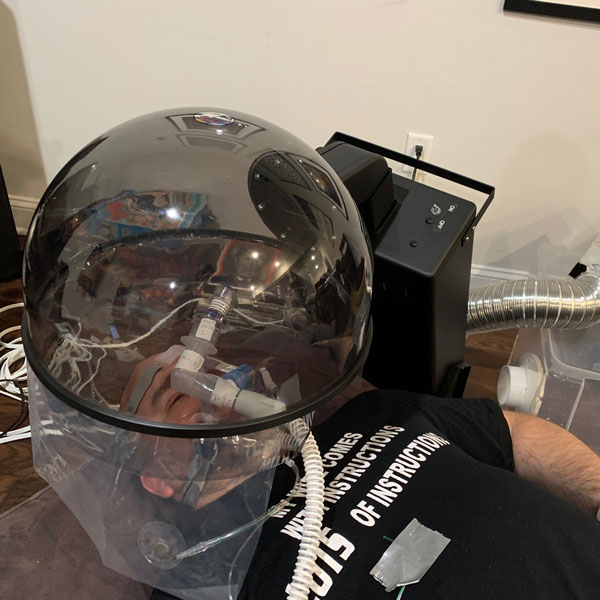
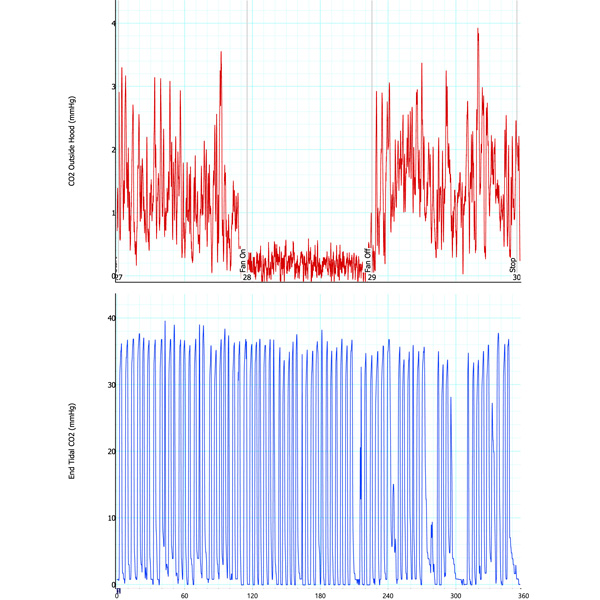
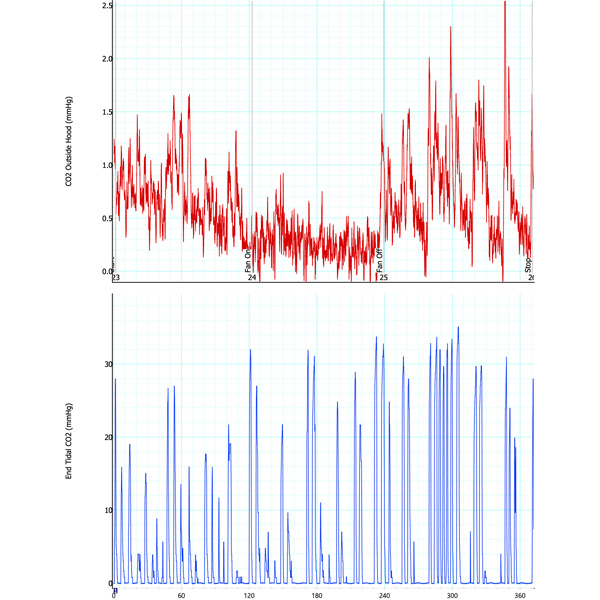
Similar to the tests with home-brewed negative pressure hood, measurements were done with the salon dryer negative pressure hood, i.e., the AirVENT. In this case, measurements were done (1) when the experimenter did not wear AirMOD (i.e., CPAP) and (2) when the experimenter wore the AirMOD. The corresponding results for the expired CO2 measurements inside the AirVENT (by the experimenter’s nose) and outside the AirVENT are given in two plots below. From each plot, it is seen that the expired CO2 measurements outside the AirVENT drop significantly when the AirVENT is turned on, illustrating the efficacy of the device to scavenge expired CO2. This demonstrates that the device can be a suitable tool in containing the spread of the aerosolized virus by a COVID-19 patient.
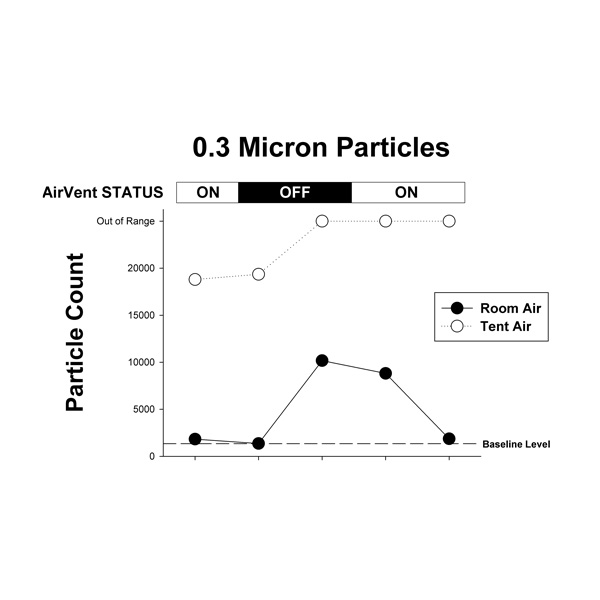
Dr. Serrador obtained a particle meter from Grainger to determine the efficacy of AirVENT in scavenging 0.3 micron particles. For baseline measurements, he determined that the room where the test was being conducted yielded a count of approximately 2K for 0.3 micron particles. Next, a fog machine was placed inside the AirVENT tent to add lots of 0.3 micron particles. This yielded a count of approximately 20K for 0.3 micron particles inside the tent. With the AirVENT off, the 0.3 micron particle count outside the AirVENT tent increased to approximately 10K. When the AirVENT was turned on, the 0.3 micron particle count outside the AirVENT tent dropped down and returned to the baseline value of approximately 2K. This illustrates the efficacy of the AirVENT fitted with a HEPA-grade filter in scavenging the 0.3 micron particles.